What if your flood insurance premium suddenly doubled, but you still weren't fully covered in the event of a disaster?
Understanding Flood Insurance Reform
Flood insurance is undergoing significant transformation as climate change increases flood risks across the United States. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), which has been the primary source of flood coverage for decades, is implementing major reforms through its Risk Rating 2.0 system. These changes are designed to more accurately reflect individual property risks while ensuring the program's financial sustainability.
Flood insurance provides critical protection for homes in flood-prone areas
The reform comes at a critical time as the NFIP faces mounting debt from increasingly frequent and severe flooding events. These changes aim to create a more equitable system where premiums better align with actual flood risks, while also encouraging mitigation efforts and expanding coverage options through the private market.
Risk Rating 2.0: A New Approach to Pricing
The centerpiece of flood insurance reform is the NFIP's Risk Rating 2.0 methodology, which represents the most significant change to flood insurance pricing in over 50 years. Unlike the previous system that primarily used flood zone maps to determine rates, Risk Rating 2.0 considers multiple factors:
- Property Specific Risks: Elevation, flood frequency, distance to water sources, and cost to rebuild
- Type of Flooding: Differentiates between riverine, coastal, and rainfall flooding
- Mitigation Features: Accounts for flood-proofing measures and community flood defenses
- Replacement Cost: More accurately reflects actual rebuilding costs
This more sophisticated approach means that some policyholders will see rate increases while others may actually see decreases. To soften the impact, most premium increases are capped at 18% annually until premiums reflect the full risk of the insured property.
Understanding Rate Changes
The transition to Risk Rating 2.0 has created significant variation in premium changes across different regions and property types:
- Low-Risk Properties: Many previously overpriced policies are seeing rate decreases
- High-Risk Properties: Some properties are experiencing substantial increases
- Coastal Areas: Properties in coastal regions often see the most significant changes
- Annual Caps: Most increases are limited to 18% per year to prevent sudden spikes
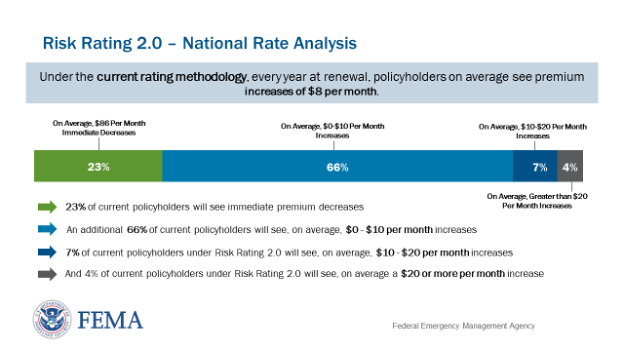
Risk Rating 2.0 has created varying rate changes across different property types
While the 18% annual cap provides some protection against sudden increases, homeowners should still budget for potential premium growth over time. Properties with the highest risk may see premiums increase by hundreds or even thousands of dollars over several years as they transition to full risk-based rates.
Expansion of Private Flood Insurance
One of the most significant aspects of flood insurance reform is the growing role of the private market. Legislative changes and regulatory reforms have created new opportunities for private insurers to offer flood insurance coverage:
- Mandatory Acceptance: Lenders must now accept private flood insurance policies that meet certain standards
- Enhanced Coverage Options: Private policies often offer higher coverage limits and additional benefits
- Competitive Pricing: The private market is becoming more competitive, especially in non-coastal areas
- Innovative Products: New parametric insurance products that pay out based on flood levels rather than damage assessments
This expansion provides homeowners with more choices and potentially better coverage options than the NFIP alone. However, private policies may not be available in all high-risk areas, and consumers should carefully compare coverage terms and pricing before making a decision.
Impact on Homeowners and Businesses
The flood insurance reforms have significant implications for both residential and commercial property owners:
- Property Values: Changing insurance costs may affect property values, especially in high-risk areas
- Mortgage Requirements: Lenders may have new requirements for flood insurance coverage
- Budget Planning: Homeowners need to account for potential premium increases in their budgets
- Mitigation Incentives: New pricing models provide stronger incentives for flood-proofing investments

Understanding flood insurance coverage options is essential for property protection
For business insurance purposes, companies with properties in flood-prone areas need to reassess their risk management strategies and consider how the reforms might affect their operations and insurance costs.
Navigating the New Flood Insurance Landscape
As the flood insurance market evolves, property owners can take several steps to ensure adequate protection:
- Review Current Coverage: Understand what your current policy covers and how it might change
- Compare Options: Shop around between NFIP and private flood insurance options
- Invest in Mitigation: Consider flood-proofing measures that may reduce premiums
- Stay Informed: Keep up with ongoing changes to flood insurance programs and requirements
- Consult Professionals: Work with insurance agents who specialize in flood coverage
By taking a proactive approach to flood insurance, property owners can better manage costs and ensure they have appropriate coverage as the landscape continues to evolve.
Conclusion: Adapting to a New Era of Flood Protection
The flood insurance reforms represent a fundamental shift in how flood risk is priced and covered in the United States. While these changes may result in higher costs for some property owners, they also create a more sustainable system that better reflects actual risks and provides more options through the private market.
As climate change continues to increase flood risks across the country, these reforms are essential for ensuring the long-term viability of flood insurance programs. By understanding the changes and taking appropriate action, property owners can navigate this new landscape and secure the protection they need for their homes and businesses.

