What would happen if your home insurance company suddenly dropped your coverage because you live in a wildfire-prone area?
Understanding Wildfire Insurance
Wildfire insurance is a specialized form of home insurance that provides coverage for damage caused by wildfires. While standard homeowners policies typically include fire coverage, insurers in high-risk areas are increasingly implementing special provisions, higher premiums, or even denying coverage altogether as wildfire risks intensify due to climate change.
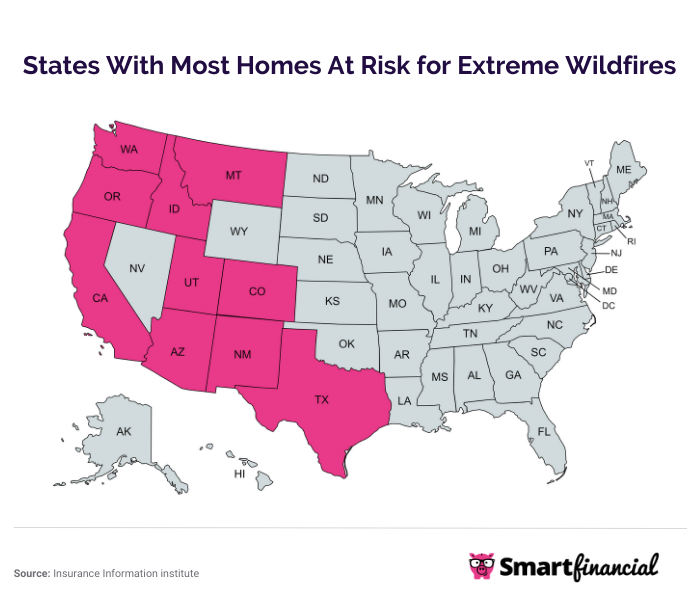
Wildfire risk varies significantly across different regions, affecting insurance availability and costs
The insurance industry's response to growing wildfire risks has created a complex landscape for homeowners in fire-prone regions. Understanding your coverage options, potential gaps, and mitigation strategies is essential for protecting your property in these high-risk areas.
Challenges in High-Risk Areas
Homeowners in wildfire-prone regions face several significant challenges when seeking insurance coverage:
- Non-Renewals: Insurers are increasingly refusing to renew policies in areas with extreme wildfire risk.
- Higher Premiums: Those who maintain coverage face dramatically increasing premiums, sometimes doubling or tripling in a single year.
- Special Deductibles: Many policies now include separate, higher deductibles specifically for wildfire damage.
- Coverage Limitations: Some policies may exclude certain types of wildfire damage or impose stricter conditions.
These challenges have created what many experts call an "insurance crisis" in states like California, Oregon, and Colorado, where homeowners struggle to find affordable coverage or any coverage at all.
Coverage Options for High-Risk Properties
Despite these challenges, several coverage options remain available for homeowners in wildfire-prone areas:
- Standard Homeowners Insurance: Still available in many areas, though often with higher premiums and special provisions.
- Specialized Wildfire Policies: Some insurers offer policies specifically designed for high-risk properties.
- Surplus Lines Insurance: Non-admitted carriers that can provide coverage when standard insurers won't.
- State FAIR Plans: Insurance pools of last resort that provide basic coverage when private insurance is unavailable.
The California FAIR Plan (Fair Access to Insurance Requirements) provides basic fire insurance for high-risk properties when traditional insurance is unavailable. While it offers essential protection, it typically provides less comprehensive coverage than standard policies and may come with higher premiums.
Mitigation Measures to Improve Insurability
Homeowners can take several steps to improve their insurability and potentially reduce premiums:
- Defensible Space: Creating a buffer zone around your home by clearing vegetation and combustible materials.
- Fire-Resistant Materials: Using fire-resistant roofing, siding, and decking materials.
- Ember-Resistant Vents: Installing vents that prevent embers from entering your home.
- Home Hardening: Reinforcing your home's structure to make it more resistant to fire.
- Community-Wide Efforts: Participating in community-level fire prevention programs like Firewise USA.
Proper mitigation measures can significantly improve a home's resistance to wildfire damage
Many insurance companies now offer premium discounts for homes that implement these mitigation measures. Some states, including California, have implemented regulations requiring insurers to offer these discounts and to consider mitigation efforts when making underwriting decisions.
Business Insurance Considerations
Businesses in wildfire-prone areas face similar challenges to homeowners:
- Property Coverage: Protecting physical assets from fire damage.
- Business Interruption: Coverage for lost income during evacuation or recovery periods.
- Contingent Business Interruption: Protection when suppliers or customers are affected by wildfires.
- Extra Expense Coverage: Coverage for additional costs to continue operations after a fire.
Business insurance for wildfire risks requires careful consideration of all potential impacts on operations, not just physical damage to property. Many businesses are now incorporating wildfire risk into their continuity planning and risk management strategies.
Legislative and Regulatory Responses
Several states have implemented legislative and regulatory responses to address the wildfire insurance crisis:
- Moratoriums on Non-Renewals: California has implemented temporary bans on non-renewals in areas affected by wildfires. Mandatory Discounts: Requirements for insurers to offer discounts for mitigation measures.
- Transparency Requirements: Rules requiring insurers to provide clearer information about coverage decisions.
- State-Sponsored Programs: Development of state-backed insurance options for high-risk properties.
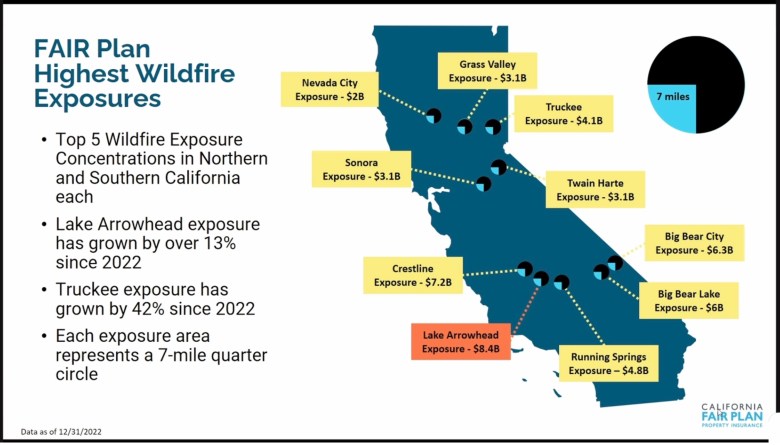
California has implemented several programs to address insurance challenges in high-risk areas
These efforts aim to balance the legitimate business concerns of insurance companies with the need to maintain affordable coverage for homeowners in high-risk areas.
Conclusion: Navigating the Wildfire Insurance Landscape
As wildfire risks continue to intensify, securing appropriate wildfire insurance has become increasingly challenging but remains essential for homeowners in high-risk areas. By understanding the available coverage options, implementing mitigation measures, and staying informed about regulatory changes, property owners can better protect their investments.
The future of wildfire insurance will likely continue to evolve as climate change impacts intensify and new solutions emerge. For now, proactive risk management and comprehensive coverage planning represent the best approach for homeowners and businesses in wildfire-prone regions.

