In today's interconnected digital landscape, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) have become the backbone of modern insurance operations, enabling seamless data exchange and service integration across disparate systems. APIs serve as digital bridges that allow different software applications to communicate with each other, facilitating the flow of information between insurers, customers, partners, and third-party service providers. From auto insurance quotes to health insurance plans, API integration is creating more efficient, connected, and customer-centric insurance operations across all segments.
Understanding API Integration in Insurance
API integration in insurance refers to the process of connecting different software systems and applications through standardized interfaces that allow them to exchange data and functionality. These interfaces define the methods and data formats that applications can use to communicate with each other, creating a seamless flow of information across the insurance ecosystem.
APIs enable insurers to break down traditional silos between systems, departments, and organizations, creating a more integrated and responsive operating environment. They allow insurers to leverage external services and data sources while maintaining control over their core systems, enabling greater flexibility and innovation without compromising security or stability.
The insurance industry has traditionally been characterized by complex, monolithic systems that were difficult to integrate with other applications. API integration represents a fundamental shift toward more modular, connected architectures that enable insurers to rapidly adapt to changing market conditions and customer expectations.
How open insurance APIs benefit insurance companies through enhanced connectivity
Types of Insurance APIs
Insurance APIs can be categorized based on their functionality and the systems they connect:
Policy Management APIs: Enable integration with policy administration systems for creating, updating, and managing insurance policies.
Claims Processing APIs: Facilitate data exchange between claims systems, adjusters, repair shops, medical providers, and other claims stakeholders.
Quoting and Rating APIs: Allow external partners and distribution channels to access real-time auto insurance quotes, home insurance quotes, and other insurance pricing.
Customer Data APIs: Enable secure access to customer information across different systems while maintaining privacy and compliance.
Payment Processing APIs: Connect insurance systems with payment gateways and banking systems for premium collection and claim payments.
Third-Party Data APIs: Integrate external data sources like weather services, vehicle history reports, and medical databases for enhanced risk assessment.
Benefits of API Integration in Insurance
API integration delivers significant benefits for insurance operations:
Enhanced Customer Experience: APIs enable seamless omnichannel experiences where customers can interact with insurers through multiple touchpoints with consistent data and functionality.
Operational Efficiency: Automated data exchange reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and accelerates processes across the insurance value chain.
Partner Ecosystem Enablement: APIs make it easier to integrate with agents, brokers, third-party administrators, and other partners, creating a more connected insurance ecosystem.
Innovation Acceleration: By providing standardized access to core systems, APIs enable faster development of new products, services, and customer experiences.
Data-Driven Decision Making: APIs facilitate the collection and analysis of data from multiple sources, enabling more informed underwriting, pricing, and risk management decisions.
Cost Reduction: Automation and streamlined processes reduce administrative overhead and operational costs.
Applications Across Insurance Segments
API integration is transforming operations across all insurance segments:
In property and casualty insurance, APIs enable real-time integration with weather services for flood insurance and earthquake insurance risk assessment, with repair shops for claims processing, and with smart home devices for preventive services. For home insurance quotes, APIs can pull property data from multiple sources to provide more accurate pricing.
For auto insurance quotes and telematics, APIs connect insurers with vehicle data providers, repair networks, and telematics platforms, enabling usage-based insurance models and streamlined claims processing. APIs also facilitate integration with DMV databases for license verification and with law enforcement for accident reporting.
Life and health insurance APIs enable integration with medical providers for health insurance plans claims processing, with wearable device providers for wellness programs, and with financial institutions for premium payments. This applies to life insurance quotes, Medicare Advantage, and specialized products like disability insurance.
Business insurance APIs connect insurers with enterprise systems for commercial auto insurance fleet management, with payroll providers for workers' compensation insurance premium calculation, and with industry-specific data sources for specialized coverage like cyber liability insurance.
Even specialized insurance products like pet insurance, travel insurance, and wedding insurance benefit from API integration with veterinary clinics, travel booking platforms, and event management services.
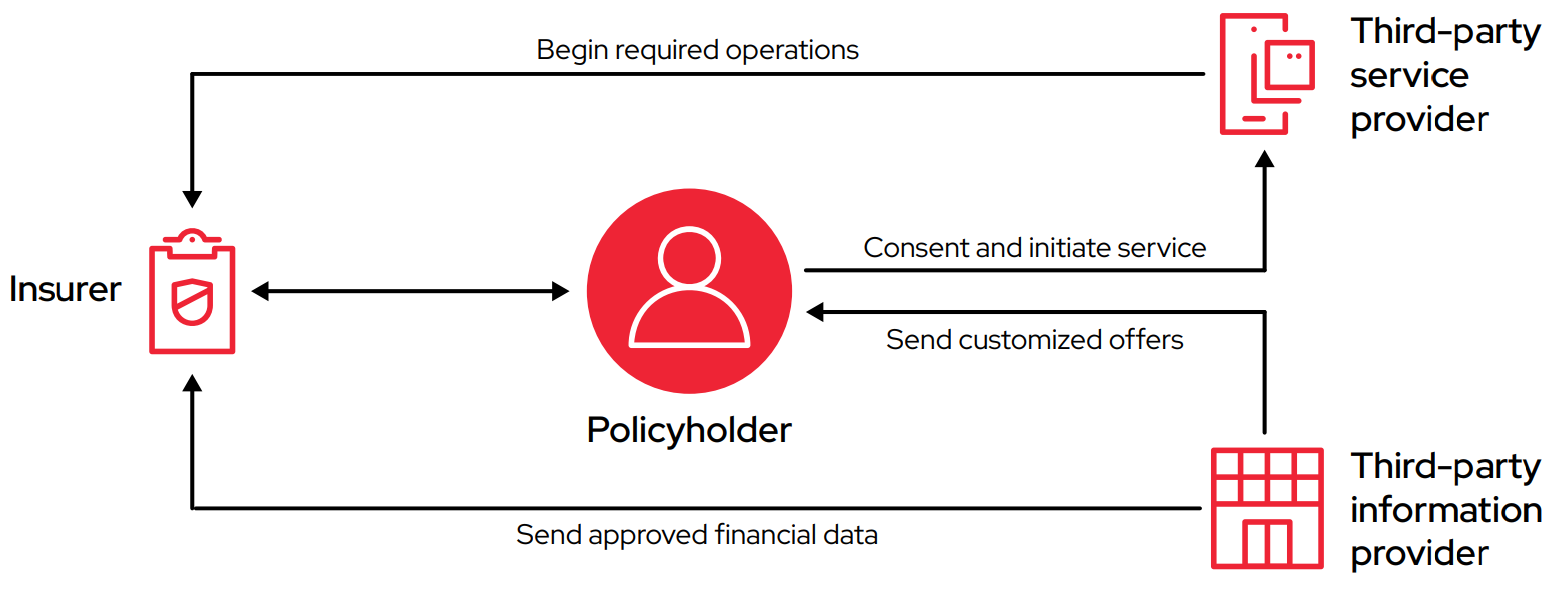
Insurance API ecosystem connecting insurers, policyholders, and service providers
Security and Compliance Considerations
While API integration offers numerous benefits, it also presents security and compliance challenges that must be addressed:
Data Security: APIs create new potential entry points for cyber attacks, requiring robust security measures including authentication, authorization, encryption, and monitoring.
Privacy Protection: Insurance APIs must comply with privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, ensuring that personal and sensitive information is properly protected.
Access Control: Implementing granular access controls ensures that different users and systems can only access the data and functionality they need.
Audit Trails: Comprehensive logging of API activities enables compliance monitoring and forensic analysis in case of security incidents.
Rate Limiting: Preventing API abuse through rate limiting and other protective measures ensures system stability and prevents unauthorized data extraction.
API Management Strategies
Effective API integration requires a comprehensive management approach:
API Gateway Implementation: Centralized management of API traffic, security, and monitoring through a dedicated gateway solution.
Developer Portal: Providing documentation, testing tools, and support for developers building integrations with insurance APIs.
Lifecycle Management: Managing APIs through their entire lifecycle from design and development to deployment and retirement.
Versioning Strategy: Maintaining backward compatibility while evolving APIs to support new functionality and requirements.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitoring API performance, availability, and usage patterns to identify and address issues proactively.
Monetization Models: Implementing appropriate monetization strategies for APIs provided to external partners and developers.
The Future of API Integration in Insurance
As technology continues to evolve, the future of API integration in insurance will be characterized by:
Open Banking/Insurance Standards: Industry-wide standards will facilitate easier integration between insurers, banks, and other financial services providers.
Event-Driven Architectures: APIs will increasingly support event-driven communication patterns, enabling real-time responses to changing conditions.
AI-Powered APIs: Artificial intelligence will be integrated into API platforms to enhance functionality like natural language processing and predictive analytics.
Blockchain Integration: APIs will connect traditional insurance systems with blockchain networks for enhanced security and transparency.
Low-Code/No-Code Integration: Simplified integration tools will enable business users to create connections between systems without extensive technical expertise.
Conclusion
API integration is fundamentally transforming the insurance industry by breaking down traditional silos and creating more connected, efficient, and customer-centric operations. By enabling seamless data exchange and service integration, APIs are helping insurers deliver faster, more personalized experiences while reducing costs and accelerating innovation.
From auto insurance quotes to health insurance plans, API integration is creating a more interconnected insurance ecosystem where data flows freely between systems, partners, and customers. The insurers who embrace API integration as a strategic priority will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly digital and connected insurance landscape.
As we look to the future, APIs will continue to evolve, incorporating emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and event-driven architectures. The most successful insurers will be those that view API integration not just as a technical implementation but as a strategic enabler of business transformation, creating new business models and revenue streams while delivering enhanced value to customers and partners.

