The insurance industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation as it embraces cloud-native technologies to build more scalable, agile, and responsive operations. Cloud-native insurance represents a shift from traditional on-premise systems to modern, cloud-based architectures that enable insurers to rapidly adapt to changing market conditions, customer expectations, and emerging risks. From auto insurance quotes to health insurance plans, cloud-native approaches are creating more efficient, flexible, and customer-centric insurance operations across all segments.
Understanding Cloud-Native Insurance
Cloud-native insurance refers to applications and systems specifically designed to run on cloud infrastructure, leveraging cloud computing's unique capabilities rather than simply migrating existing systems to the cloud. This approach embraces microservices architecture, containerization, continuous delivery, and DevOps practices to create systems that are inherently scalable, resilient, and adaptable.
Unlike traditional monolithic insurance systems that are difficult to modify and scale, cloud-native architectures break down functionality into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This modular approach enables insurers to innovate faster, respond to market changes more quickly, and deliver new products and services with greater agility.
The cloud-native approach also provides significant cost advantages by eliminating the need for extensive on-premise infrastructure, reducing maintenance overhead, and enabling more efficient resource utilization through pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Latest cloud technology trends transforming the insurance industry
Key Technologies Enabling Cloud-Native Insurance
Several technologies are at the core of cloud-native insurance operations:
Microservices Architecture: Breaks down monolithic applications into small, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Containerization: Packages applications and their dependencies into lightweight, portable containers that can run consistently across different environments.
Container Orchestration: Automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, with Kubernetes being the most popular platform.
DevOps and Continuous Delivery: Enables rapid, reliable software delivery through automation of build, test, and deployment processes.
API-First Design: Creates systems with well-defined APIs that enable easy integration between services and with external partners.
Serverless Computing: Allows insurers to run code without managing servers, paying only for actual compute resources consumed.
Benefits of Cloud-Native Insurance Operations
Cloud-native approaches deliver significant benefits for insurance operations:
Scalability: Systems can automatically scale up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak periods without overprovisioning.
Agility: New features and products can be developed and deployed in weeks rather than months, enabling faster response to market opportunities.
Resilience: Distributed architecture with built-in redundancy ensures high availability and quick recovery from failures.
Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing models eliminate the need for large upfront infrastructure investments and reduce total cost of ownership.
Innovation Enablement: Cloud platforms provide access to advanced services like AI/ML, big data analytics, and IoT integration without significant upfront investment.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Faster development cycles enable more responsive, personalized customer interactions across all touchpoints.
Applications Across Insurance Segments
Cloud-native approaches are transforming operations across all insurance segments:
In property and casualty insurance, cloud-native platforms enable more flexible home insurance quotes and policy management systems that can quickly adapt to changing risk models and regulatory requirements. For flood insurance and earthquake insurance, cloud-based systems can integrate with real-time weather data and IoT sensors to provide more accurate risk assessment and pricing.
For auto insurance quotes and telematics, cloud-native architectures can handle the massive volume of data generated by connected vehicles, enabling real-time risk assessment and personalized pricing. The scalability of cloud platforms is particularly valuable for usage-based insurance models that process continuous streams of telematics data.
Life and health insurance benefit from cloud-native systems that can securely manage sensitive health data while providing the computational power needed for complex underwriting models. This applies to life insurance quotes, health insurance plans, and specialized products like Medicare Advantage and long-term care insurance.
Business insurance operations are enhanced through cloud-native platforms that can integrate with various business systems, providing comprehensive risk management solutions for commercial auto insurance, general liability insurance, and workers' compensation insurance.
Even specialized insurance products like cyber liability insurance, pet insurance, and travel insurance benefit from the flexibility and scalability of cloud-native architectures.
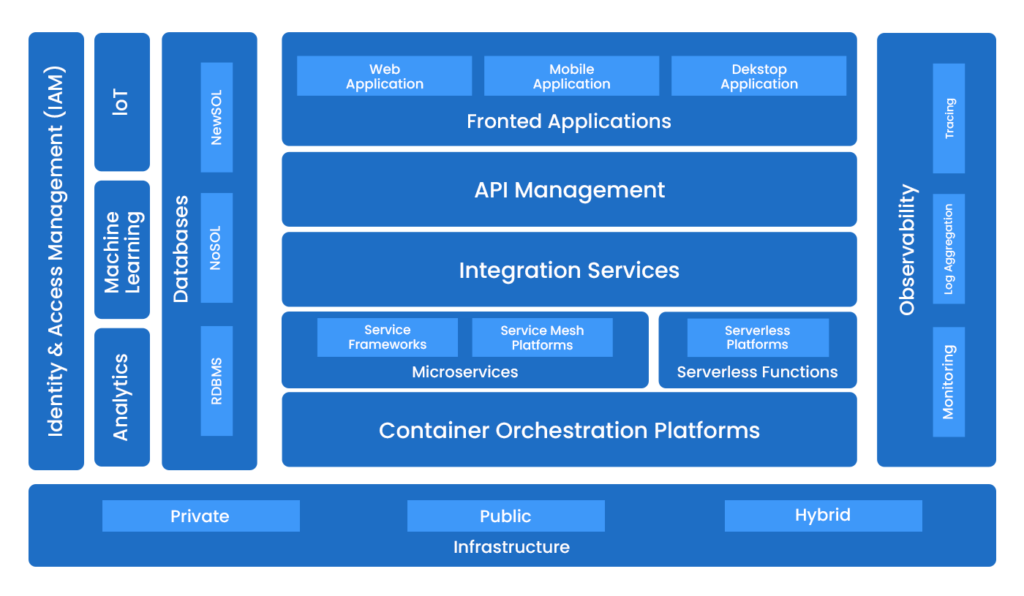
Cloud-native technology architecture showing infrastructure, container orchestration, and microservices
Transforming the Customer Experience
Cloud-native insurance operations directly enhance the customer experience through:
Faster Service Delivery: Customers can receive auto insurance quotes, policy documents, and claim payments in seconds rather than days.
Personalization at Scale: Cloud-based analytics and AI capabilities enable highly personalized product recommendations and pricing based on individual customer data.
Omnichannel Experience: Cloud-native platforms provide consistent experiences across web, mobile, and in-person channels, with real-time synchronization of customer data.
Self-Service Capabilities: Customers can manage their policies, file claims, and track progress through intuitive digital interfaces available 24/7.
Proactive Engagement: Cloud platforms enable insurers to analyze customer behavior and reach out with relevant offers and risk mitigation advice at the right time.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, implementing cloud-native insurance operations presents several challenges:
Legacy System Migration: Transitioning from established on-premise systems to cloud-native architectures requires careful planning and execution.
Skills Gap: Cloud-native development requires specialized skills that may be scarce within traditional insurance organizations.
Data Security and Compliance: Insurance companies must ensure that cloud implementations meet strict regulatory requirements for data protection and privacy.
Cultural Transformation: Adopting cloud-native approaches requires significant cultural change, moving from traditional siloed development to collaborative, cross-functional teams.
Vendor Lock-In: Insurers must carefully manage their relationships with cloud providers to avoid excessive dependency on specific platforms.
The Future of Cloud-Native Insurance
As cloud technology continues to evolve, the future of cloud-native insurance will be characterized by:
AI-Driven Operations: Cloud platforms will increasingly integrate AI and machine learning capabilities throughout the insurance value chain.
Edge Computing: Processing will move closer to data sources, enabling real-time decision making for IoT-based insurance products.
Industry-Specific Cloud Solutions: Cloud providers will offer more specialized services tailored to insurance industry needs.
Composable Architecture: Insurers will build systems from interchangeable business capabilities, enabling even greater flexibility and innovation.
Quantum-Ready Infrastructure: Cloud platforms will prepare for the eventual integration of quantum computing for complex risk modeling.
Conclusion
Cloud-native insurance represents more than just a technological shift—it's a fundamental transformation of how insurance companies operate, innovate, and serve customers. By embracing cloud-native architectures, insurers can build more scalable, agile, and responsive operations that are better equipped to navigate the rapidly changing insurance landscape.
From auto insurance quotes to health insurance plans, cloud-native approaches are enabling insurers to deliver more personalized, efficient, and valuable experiences to customers while reducing operational costs and increasing innovation capacity. The insurers who successfully make this transition will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive and digital-first insurance market.
As we look to the future, cloud-native insurance will continue to evolve, incorporating emerging technologies like AI, edge computing, and quantum computing. The most successful insurers will be those that view cloud transformation not as a one-time project but as an ongoing journey of continuous improvement and innovation.

