The healthcare landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation with the shift from traditional fee-for-service models to value-based care insurance. This innovative approach to healthcare delivery and payment prioritizes quality over quantity, incentivizing providers to deliver the best possible outcomes for patients rather than simply performing more procedures. As this model continues to gain momentum, understanding how value-based care insurance works and its potential benefits can help you make more informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Value-Based Care vs. Traditional Fee-for-Service
Traditional healthcare operates on a fee-for-service model, where providers are paid for each test, procedure, and visit they perform. This system creates financial incentives for more services rather than better outcomes, often leading to fragmented care and unnecessary treatments.
In contrast, value-based care insurance models tie payments to quality metrics and patient outcomes. Providers are rewarded for keeping patients healthy, preventing chronic diseases, and efficiently managing existing conditions. This approach aligns the financial interests of providers, insurers, and patients, creating a more coordinated and effective healthcare system.
The fundamental equation of value-based care is simple: Value = Quality ÷ Cost. By maximizing quality while minimizing costs, this model aims to deliver better health outcomes at lower overall expenses.
Types of Value-Based Care Arrangements
Several models of value-based care insurance have emerged, each with unique approaches to rewarding quality outcomes:
Benefits of Value-Based Care for Patients
The shift to value-based care insurance offers numerous advantages for patients:
Better Health Outcomes: With a focus on quality and prevention, patients experience improved health outcomes and better management of chronic conditions.
Coordinated Care: Value-based models emphasize care coordination among different providers, reducing redundant tests and conflicting treatments.
Preventive Services: Providers are incentivized to offer preventive care and early intervention, potentially avoiding more serious health issues down the road.
Lower Costs: By eliminating unnecessary procedures and focusing on efficient care, value-based models can help reduce overall healthcare expenses for patients.
Enhanced Patient Experience: With an emphasis on patient satisfaction and engagement, value-based care often leads to better communication and more personalized treatment plans.
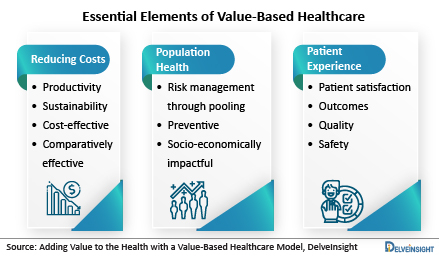
Benefits for Healthcare Providers and Insurers
Providers and insurers also benefit from value-based care insurance models:
Financial Incentives: Providers can earn bonuses or share in savings by delivering high-quality, efficient care.
Reduced Administrative Burden: Coordinated care models often streamline administrative processes and reduce paperwork.
Predictable Revenue: Capitation and bundled payment models provide more predictable revenue streams compared to fee-for-service.
Improved Population Health: By focusing on preventive care and chronic disease management, providers can improve the overall health of their patient populations.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that excel in value-based care can differentiate themselves in an increasingly competitive healthcare market.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, implementing value-based care insurance comes with challenges:
Quality Measurement: Developing fair and accurate metrics to measure quality and outcomes can be complex and controversial.
Initial Investment: Transitioning to value-based models often requires significant upfront investment in technology, infrastructure, and staff training.
Risk Adjustment: Properly adjusting payments based on patient risk factors is essential to ensure providers aren't penalized for treating sicker populations.
Data Integration: Effective value-based care requires robust data systems to track outcomes, coordinate care, and measure performance.
Provider Participation: Some providers may be hesitant to adopt value-based models due to financial uncertainty or lack of resources.
Finding Value-Based Care Insurance Options
As value-based care insurance becomes more prevalent, consumers have more options to choose from:
Medicare Advantage Plans: Many Medicare Advantage plans have embraced value-based care models, offering additional benefits and lower out-of-pocket costs for high-quality care.
Employer-Sponsored Plans: An increasing number of employers are offering health plans that incorporate value-based care principles.
Direct Primary Care: Some patients are opting for direct primary care arrangements where they pay a monthly fee for comprehensive primary care services.
ACO Participation: When selecting healthcare providers, consider whether they participate in Accountable Care Organizations or other value-based initiatives.
Quality Ratings: Look for plans and providers with high quality ratings from organizations like the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA).
The Future of Value-Based Care
The future of value-based care insurance looks promising, with several emerging trends:
Expanded Adoption: Value-based models continue to gain traction across both public and private insurance sectors.
Advanced Analytics: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are enhancing the ability to measure outcomes, predict risks, and personalize care.
Social Determinants of Health: Increasing recognition of how social factors impact health outcomes is leading to more holistic approaches to care.
Patient Engagement: Digital tools and wearable devices are empowering patients to take a more active role in their healthcare.
Specialty Care Integration: Value-based models are expanding beyond primary care to include specialty services and hospital care.
Final Thoughts
Value-based care insurance represents a paradigm shift in how healthcare is delivered and paid for, with the potential to improve quality while controlling costs. By aligning financial incentives with patient outcomes, this model promises a more sustainable and effective healthcare system.
As a consumer, understanding value-based care can help you make more informed decisions about your health insurance plans and healthcare providers. Look for plans and providers that emphasize quality outcomes, care coordination, and preventive services. When evaluating options, consider not just the immediate costs but also the potential long-term benefits of better health outcomes.
The transition to value-based care is ongoing, but its momentum is undeniable. By embracing this quality-focused approach to healthcare, we can work toward a system that delivers better outcomes, improved patient experiences, and more sustainable costs for everyone involved.

